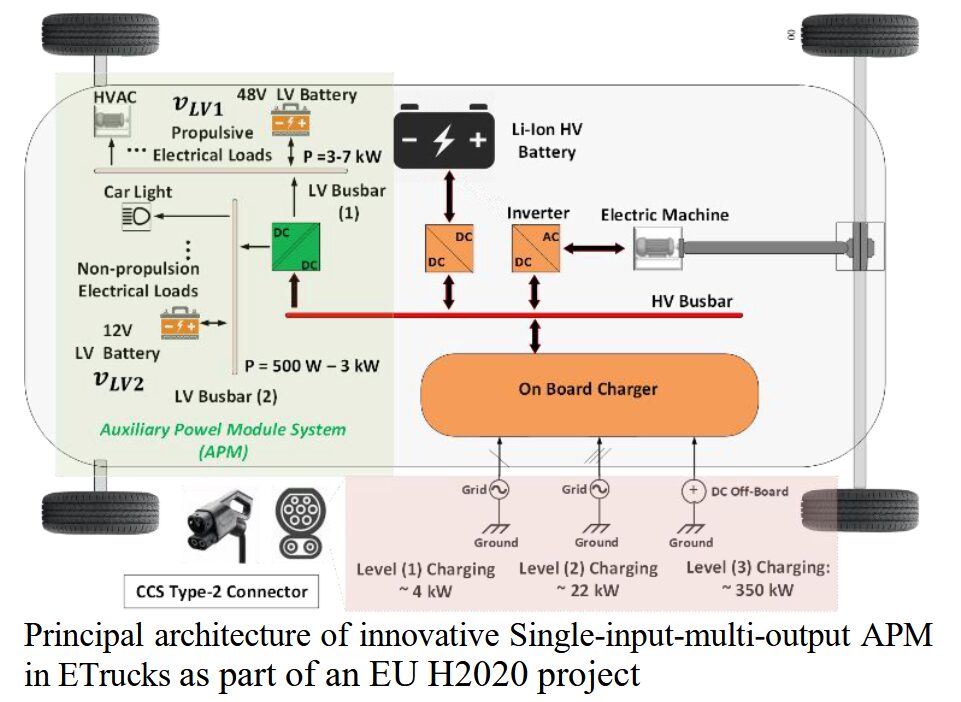
The research paper, “Efficient and Bidirectional Cascaded Auxiliary Power Module Design for Electric Trucks Using Hybrid Si, SiC, and GaN Technologies” was recently published by the Brussels-based NextETRUCK consortium partner of VUB and explores advanced power solutions for electric trucks. It highlights the growing demand for efficient auxiliary power modules (APMs) to support various truck systems, such as air conditioning, emergency braking, and onboard electronics. The study emphasizes the shift from traditional 12V systems to 48V systems for better energy efficiency and reliability, especially in medium and heavy-duty battery electric vehicles (BEVs).
The development of APMs is pivotal for advancing the capabilities of battery-electric heavy-duty trucks. The shift to higher voltage auxiliary systems, such as the 48V standard, not only reduces power losses but also enhances the vehicle’s overall reliability and efficiency. These innovations play a crucial role in accelerating the adoption of battery-electric heavy-duty trucks by meeting the industry’s stringent performance and reliability standards, while also supporting global sustainability goals.
The publication addresses the design and validation of an innovative APM system, crucial for power distribution in electric trucks. The proposed APM integrates two stages: an isolated Dual Active Bridge (DAB) converter for stepping down from a high-voltage (HV) battery to a 48V system, and a non-isolated synchronous interleaved buck-boost converter for further reduction to a 12V system.
This APM design represents a critical step toward achieving reliable, efficient, and modular power distribution systems for electric trucks, aligning with the European Union’s sustainability goals. The findings provide valuable insights into the optimization of BEV auxiliary systems for future applications.